Inferior Calcaneal Spur Symtoms

Overview
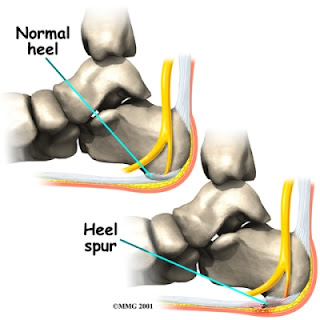
A heel spur is a hooked bony growth protruding from the calcaneus or heel bone. It often occurs alongside plantar fasciitis, and as such the two conditions are often confused, however they are not the same.
Causes
Fctors that increase the risk of developing heel spurs include a high body mass index (BMI), regular vigorous activity, and intensive training routines or sports. Factors such as these are believed to increase the incidence of repetitive stress injuries that are associated with the formation of heel spurs. When a heel spur forms, extremely sharp pain along with the feeling that a part of the heel is trying to burst through the skin usually occurs. If left untreated, an individual may eventually begin to struggle to perform simple activities such as walking.
Symptoms
Heel spurs may or may not cause symptoms. Symptoms are usually related to the plantar fasciitis. You may experience significant pain. Your heel pain may be worse in the morning when you first wake up or during certain activities.
Diagnosis
Your doctor, when diagnosing and treating this condition will need an x-ray and sometimes a gait analysis to ascertain the exact cause of this condition. If you have pain in the bottom of your foot and you do not have diabetes or a vascular problem, some of the over-the-counter anti-inflammatory products such as Advil or Ibuprofin are helpful in eradicating the pain. Pain creams, such as Neuro-eze, BioFreeze & Boswella Cream can help to relieve pain and help increase circulation.
Non Surgical Treatment
Some heel spurs do require surgery, however surgery is a last resort. In most cases the patients underlying foot problem needs to be addressed, such as Over Pronation and Over Supination and Heel Pain Treatment Options need to be implemented if Plantar Fasciitis and Achilles Tendonitis are still an ongoing concern. Your best treatment is always prevention.
Surgical Treatment
More than 90 percent of people get better with nonsurgical treatments. If conservative treatment fails to treat symptoms of heel spurs after a period of 9 to 12 months, surgery may be necessary to relieve pain and restore mobility. Surgical techniques include release of the plantar fascia, removal of a spur. Pre-surgical tests or exams are required to identify optimal candidates, and it's important to observe post-surgical recommendations concerning rest, ice, compression, elevation of the foot, and when to place weight on the operated foot. In some cases, it may be necessary for patients to use bandages, splints, casts, surgical shoes, crutches, or canes after surgery. Possible complications of heel surgery include nerve pain, recurrent heel pain, permanent numbness of the area, infection, and scarring. In addition, with plantar fascia release, there is risk of instability, foot cramps, stress fracture, and tendinitis.